Green process
Environmental Impact Data Summary (FY2024)
-
[Range of applicability of data]
Yaskawa Electric and group companies and partners within Yaskawa Electric business sites, Yaskawa Motor Corporation
However, the ranges of the following items are defined separately.
“Green process” to reduce the burden on the environment in business activities
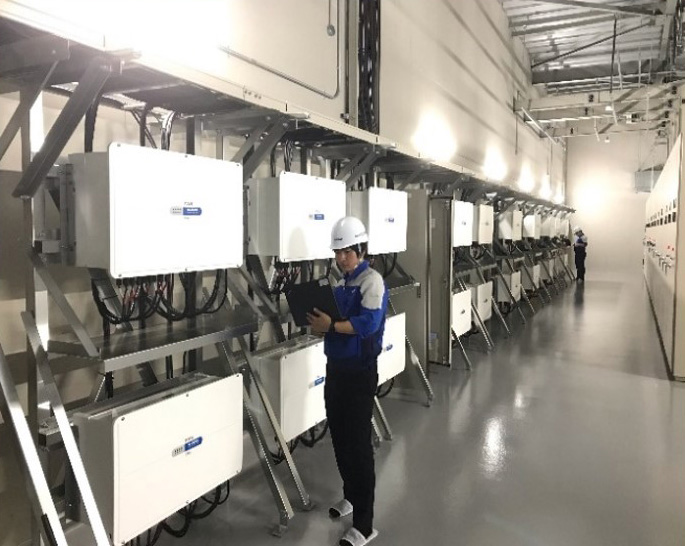
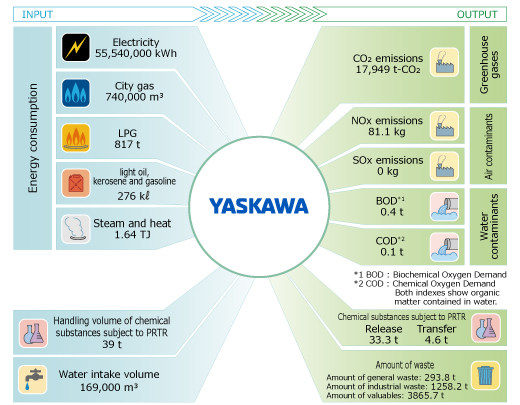
The Yaskawa Group emits CO2 and waste materials as a result of using energy, such as electricity, gas, etc., and resources, such as components/materials, water, etc., for manufacturing, sales, engineering, etc., of electrical products and systems, and other related businesses.
The above figure illustrates the status of environmental loads of our production and sales activities.
We also manage the amount of energy used, CO2 emissions, and amounts of waste materials and valuables generated from business activities of our domestic and international group companies.
The scope of management targets group companies of high energy usage amount (accounting for approximately 99% of the energy used by the entire group).
Going forward, we shall promote the reduction of environmental loads.
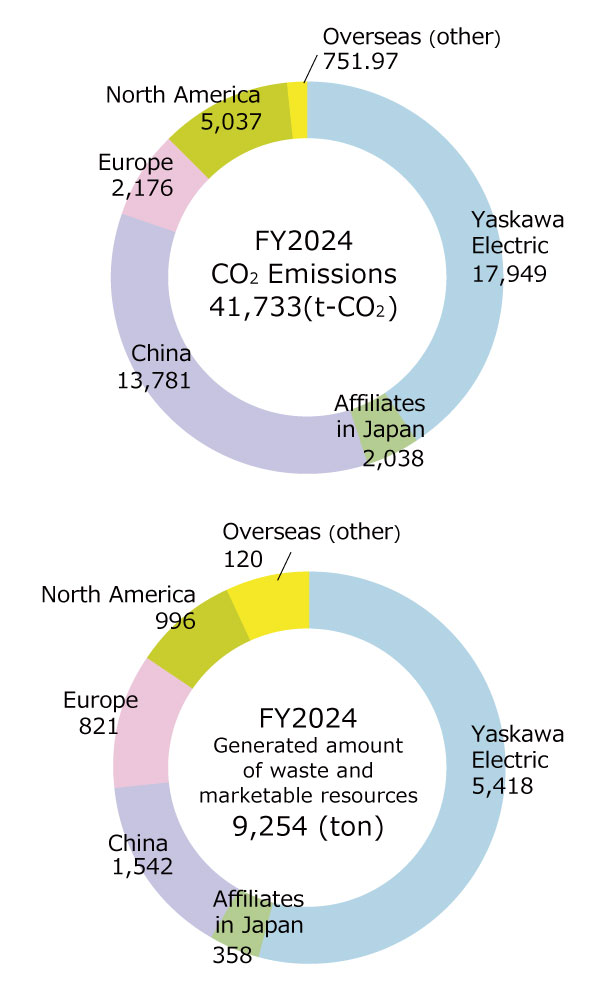
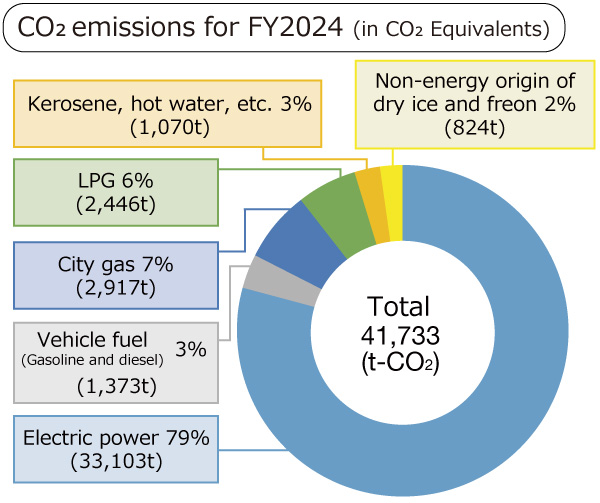
The graph at the right shows the energy-derived CO2 emissions of the Yaskawa Group in FY2024.
Measures against Climate Change
Initiatives to Save Energy
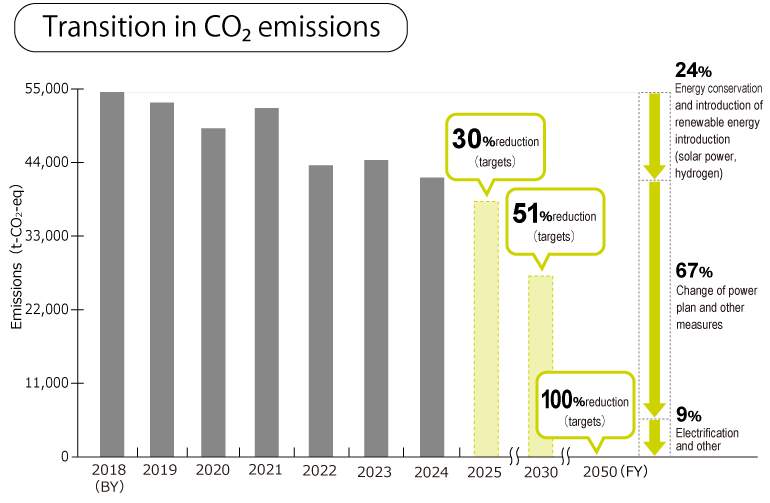
Yaskawa engaged in energy-conservation activities with the aim of reducing total Group CO2 emissions by 15% (compared to FY2018), as per the target in the 2024 Midterm Environmental Plan.
In FY2024, Yaskawa mainly advocated for improvements to investigate and prevent air leakages, as well as upgrade lighting and air-conditioners.
In addition, the introduction of solar power systems with capacities of 2,755 kW at the Shenyang plant and 4,150 kW at the Changzhou plant in China resulted in a 23.4% reduction in total Group CO2 emissions in FY2024, achieving the target.
-
-
*Actual emission factors released by electric power companies were used until FY2018 to calculate CO2 emissions from electric power in Japan. Adjusted emission factors are used from FY2019 onward.
*For calculation of CO2 emissions from electric power overseas, the representative emissions factor of each country (see IEA data) is used.
[Range of applicability of data] Yaskawa Group
Initiatives to Decarbonize Electricity
Under its 2025 Midterm Environmental Plan, the Group aims to reduce CO2 emissions by 30% (compared to FY2018) and reach a CO2-free energy rate of 75% or more in electricity usage.
In February 2025, we completed the adoption of CO2-free energy at Yukuhashi Plant, in addition to Yahata-nishi Plant, Nakama Plant, Kokura Plant, and Iruma Plant.
As a result, CO2-free energy makes up approximately 63% of our energy consumption.
Achievement of Carbon Neutrality (zero CO2 emissions) at the Chubu Robot Center
Chubu Robot Center CO2 Zero Power Certificate
In May 2024, the Chubu Robot Center entered into a contract for the CO2-free plan offered by Chubu Electric Power. The electricity purchased now is generated without CO2 emissions in accordance with non-fossil fuel energy certificates. Since electricity accounts for 100% of the plant’s energy, the Chubu Robot Center is Yaskawa’s first site to achieve zero CO2 emissions. The certificate granted for using zero CO2 energy is posted at the entrance of the Chubu Robot Center.
Startup of Solar Power System at Robot Plant No.4
The solar power generation system at Plant No.4, which was completed in August 2023, has started operation. The solar panel capacity is 822 kw, the largest of Yaskawa’s solar power systems.
The photovoltaic solar inverter used for the system is the new Enewell-SOL P3A, which was released in 2023.
Energy-Saving Proposals for Suppliers
Based on our YASKAWA ECO VISION, we are strengthening initiatives aimed at realizing a decarbonized society. As part of these efforts, we conduct energy-saving diagnoses for suppliers and provide specific improvement proposals.
Main proposals:
– Optimizing air-conditioning operation patterns, saving energy through equipment improvements, improving air leakages, ensuring proper operation of exhaust fans, installing shading nets on outdoor units, supporting the introduction of solar power systems.
With these proposals, we aim to help suppliers reduce energy consumption, lower CO2 emissions, and optimize electricity costs. We consider it our mission to reduce environmental impact across our entire supply chain and will continue to provide ongoing support.
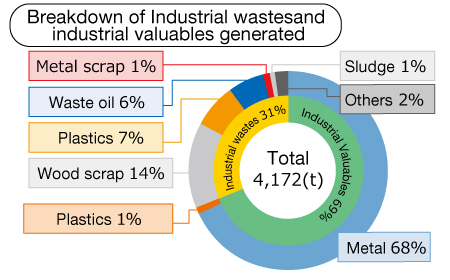
Resource Recycling and Resource Saving
We are committed to realizing a circular society by reducing waste and recycling resources. Throughout the entire life cycle of our products and services, we work to reduce environmental impact and promote the 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) for waste, including plastics.
We also ensure proper management of chemical substances contained in our products and comply with all relevant laws and regulations in Japan and overseas. From manufacturing to disposal, we strive to minimize environmental impact and prevent pollution caused by leakage or improper disposal of chemical substances.
Recycling Activities
As a result of China’s plastic waste import restrictions, waste plastics, which were conventionally sold as valuable materials, are now classified as waste.
However, by selecting a recyclable waste disposal operator, we were able to maintain zero waste emissions.
Packing Materials Information
Policy on Water Usage
The Yaskawa Group recognizes that water is a limited resource and strives to protect water resources.
Water Usage Management
Water usage is monitored monthly to make sure that water leakage and other problems are detected early.
We promote the installation of real-time remote monitoring equipment when constructing new buildings.
Additionally, at our headquarters rainwater accounts for 97% of the total water amount used.
No violations or penalties occurred with regard to laws and regulations concerning water usage during FY2024.
Initiatives to Reduce Water Withdrawal
Our production processes do not rely heavily on water, and most of our water withdrawal is for human consumption and sanitary purposes.
We are working to reduce water withdrawal by taking measures against water leakage and switching to water-saving equipment.
In particular, we are actively promoting the use of water-saving toilets and other measures to reduce water consumption when constructing new buildings.
Evaluation of Water Risks
We evaluate water risks at the Yaskawa Group’s production plants in Japan and overseas using “Aqueduct”*1.
Evaluations indicated that six plants in China and one plant in India are located in high water stress areas. In FY2024, water withdrawal at sites located in areas with high water stress totaled 27,100 m3, accounting for 10% of the entire Yaskawa Group.
Water storage tanks are installed at sites with risk of drought, and sandbags and water barriers are placed at sites with risk of flooding.
*1: Water risks refer to the dangers and threats to corporate activities that may result from water pollution and water stress due to water shortages.
Initiatives of 3R(Reduce・Reuse・Recycle)
・Reuse of isopropyl alcohol (IPA)
High-purity IPA had been discarded from the Bestact Solutions’ Bestact manufacturing line in the Yukuhashi plant.
As a result of a review conducted by the group companies within Yukuhashi Plant, mainly centering on Yaskawa Electric, reuse of IPA was started because the quality of IPA used in Yaskawa Controls’s repair process could be ensured.
Consequently, the activities resulted in significant improvement in the amount of IPA discarded from 3,500 liters per year to 500 liters per year.
 Region
Region



 Principles & vision
Principles & vision
 Procurement
Procurement
 Sustainability for the Yaskawa Group
Sustainability for the Yaskawa Group
 Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction
 Supply chain
Supply chain
 Social contribution
Social contribution
 Compliance & risk management
Compliance & risk management